Want to know what Spread Betting is, how it works, its advantages & disadvantages and how to use it to trade the markets? Then, take 5 minutes to read this guide.
We’ve put together a useful guide to tell you all about what spread betting is, how it works, and its advantages and disadvantages. Read on to find out more about how to spread bet on financial markets in the UK.
With our spread betting guide, we give you usable insight into the basics of spread betting. This kind of derivatives trading involves speculating on the price movements of financial markets. If the underlying instrument moves in the way you predicted, you’ll make a profit.
Spread betting is very popular among traders in the UK, thanks to its tax-free status and other factors. While this may sound attractive, we recommend that you spend a bit of time learning how financial spread betting works before you jump in – so we put together this guide to help you do exactly that.
What is Spread Betting?
Spread betting is a derivative that allows you to speculate on the price movements of financial instruments, such as currencies, indices, commodities, and stocks, without owning the underlying asset.
For example, instead of buying an amount of the asset (such as one lot or 1,000 shares), you place a stake per point to win (or lose) for every point the market moves up or down.
Spread betting is regulated by the Financial Conduct Authority in the United Kingdom and is considered a form of gambling not trading.
How To Learn Spread Betting
How do you join the ranks of spread bettors in the UK? Before you begin trading for real, you’ll need to take a couple of preliminary steps.
We’ve outlined these for you below.
Research
We always advise that you build your knowledge before you start trading. So research is a good place to begin.
The first stage of your research will be geared towards finding the best spread betting brokers for you as a trader.
Here’s what you’ll need to consider:
- Reviews from industry experts and from other users.
- Regulation – You should only work with spread betting brokers who are regulated by the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA).
- The financial markets the broker offers for spread betting
- The trading platforms available – For example, MetaTrader 4 or TradingView.
- The spreads – Tighter spreads equal lower trading costs.
- The execution speed.
- The account types available.
- The customer support provided.
Practice
Once you’ve found a broker that matches what you need, the next step is to practice on the broker’s demo account.
This is a risk-free account, where you’ll trade with virtual money rather than your own funds. We believe this is an absolute must for anyone starting out in trading, or using a new trading platform for the first time.
You won’t need to commit to any particular broker just yet. Instead, you can spend time getting used to the features and learning if the broker is right for you.
Getting Started with Spread Betting
With some preliminary research under your belt, you can take steps towards spread betting for real. Remember, you can keep using your demo account whenever you need to – for instance, if you want to try out a new strategy.
1. Open a Spread Betting Account
Many brokers offer multiple account types. You’ll need to make sure you choose an account type that enables you to spread bet.
2. Research Spread Bet Strategies
One of the things we like the best about spread betting is that you can use different strategies to target potentially profitable markets.
We’ve listed a few of the more popular strategies below:
- Swing trading – This is a trend-following strategy where you aim to spot the low and high swings of the market trend, in search of reversal points.
- Scalping – This is a strategy that uses leverage to take advantage of small price movements over a short timeframe. You’ll keep your bet open for just seconds or minutes at a time, hopefully taking small profits, but often.
- Breakout trading – Breakout trading involves entering a position after the market breaks above a strong resistance or support level. This “breakout” will hopefully be strong enough to carry the price further, so you can profit from it.
- Price action trading – This is a form of analysis that seeks chart and candlestick patterns that indicate a potential price reversal.
3. Decide On A Market To Spread Bet On
From currencies, indices, commodities and shares, there are various financial markets available to you when spread betting. Some brokers, such as Spreadex, also offer spread betting on sports.
Here is some advice from SpreadBet co-founder Noam Korbl:
“All markets behave differently, so I recommend choosing just one market to focus on and gain experience with that asset,” Noam says.
“This is because each market has its own patterns and behaviours, which is why I think it’s best to become an expert in one market, and one market alone, as you start out.”
4. Set Your Stake Size
With spread betting, you set a bet size (or stake) that you want to risk for every point the market moves.
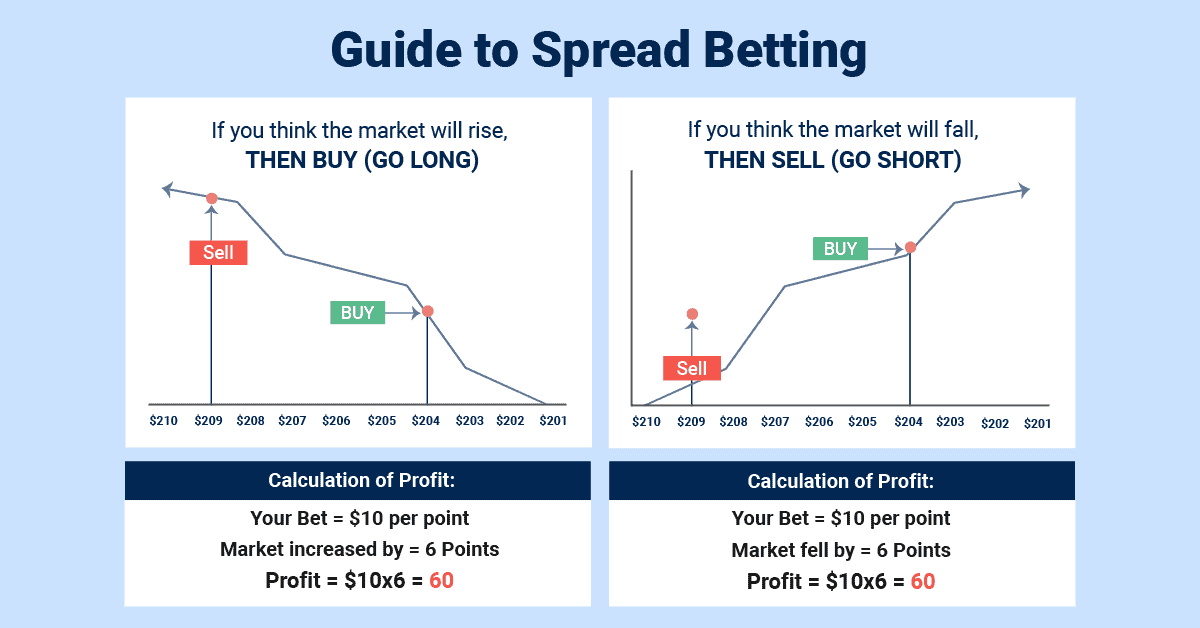
For example, setting your bet size to £10 means you will profit or lose £10 for every point the market moves. If the market moves 10 points higher, you will make £100. If the market falls 5 points against you, you will lose £50.
5. Choose To Buy Or Sell
As a derivative, spread betting allows you to speculate on market movements without owning the underlying asset. You can go long if you anticipate a rise, or go short if you expect a fall.
This means you’ve got opportunities for short-term trading and capitalising on daily volatility, regardless of market direction.
To open your bet, you must choose to go long (buy) or short (sell).
Enter your stake size, which is the amount you wish to risk per point. Then, your deal ticket will show you how much margin is required to open the bet.
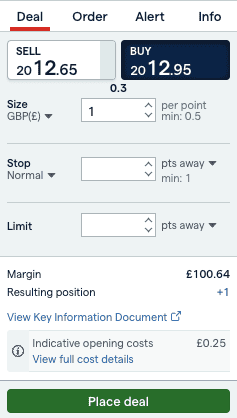
As you can see in the example above, my deal ticket shows I will be buying gold at $2012.95 and staking £1 per point, with a margin requirement of £100.54 to open the bet.
6. Apply Risk Management Tools
Spread betting is considered a high-risk trading activity, because it uses leverage and margin to open bets which can amplify profits and losses on small market movements.
This is why we seriously recommend strong risk management. Brokers provide a number of different tools you can use to manage your risk including:
- Stop Loss Orders will automatically close your position if it falls to a specific price, limiting your losses if the market moves against you.
- Take Profit Orders will automatically close your position once it rises to a specific price. This order helps you lock in your profits when the market moves in your favour. Take profit allows you to capitalise on your bets if you are away from your computer, or if the market is particularly volatile.
Noam Korbl also suggests another risk management tool – guaranteed stop-loss orders:
“For me, stop loss and take profit orders are absolute must haves,” he said.
“However, a guaranteed stop-loss order is my top recommendation. For a premium, this will ensure you won’t lose extra money due to slippage or gapping – as long as the broker offers
7. Action Your Bet
All that’s left is to review your spread bet parameters and then place your deal. The broker will make this simple and straightforward, with a clear button to press once you want to open the bet.
Why Spread Bet?
There are various benefits to spread betting. While there are some risks to be aware of, the preferential tax treatment and wide range of markets available can make it an attractive proposition.
Below we have outlined some of the pros and cons of spread betting:
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Exempt from capital gains tax and stamp duty for UK residents | Cannot claim losses against tax |
| Can go long and short | Open positions have daily financing fees |
| Accounts are in GBP removing currency risk of USD-based accounts | Less pricing transparency than CFDs |
| Can use leverage | Limited investor protections |
| Negative balance protection | Volatility risks |
How Does Spread Betting Work?
Spread betting markets involve several important elements, including the spread, stake size, margin, and leverage. Below, we breakdown these elements, to give you a better understanding:
- Spread: The spread is the difference between the buy (bid) price and the sell (ask) price of a financial instrument. It represents the broker’s profit. When you enter into a spread bet, you do so at the current sell price – if the market moves beyond the spread in your desired direction, the trade will be profitable.
- Direction: The market can only go up or down. You decide whether to go long (buy) or go short (sell), based on your market analysis and prediction about the future price movement of an asset.
- Stake Size: The stake size is the amount of money you are willing to bet per unit of price movement. These units are referred to as pips in forex. The larger the stake size per pip, the greater the potential profit or loss you will incur.
- Margin: Is the initial deposit required by the broker to open a spread bet. It is a percentage of the total position size, and serves as a security against potential losses. Leverage is used to control a larger position with a smaller amount of capital – the margin tells you how much of your own money you’ll need to put down.
- Leverage: Allows you to control a more substantial position, often many multiples of your own capital. The maximum leverage for forex spread betting is 1:30, which means you can control a position worth £30,000 using only £1,000 of your own money. While leverage can amplify profits, it also increases the risk of significant losses.
Spread Betting Examples
A spread bet broker will quote a two-way price, and you will be able to bet whether that asset’s price will move up or down. You’ll bet a stake for each point of movement.
Below, we provide a few examples to demonstrate how a spread betting trading strategy can work in action:
Example 1. Winning Bet
A winning spread bet trade
- The FTSE 100 market is quoted at 4200 – 4202
- You have the option of buying at 4202 (the offer price), or selling at 4200 (the bid price)
- You expect the price to move up, so you buy at 4202, risking £1 a point
- The prediction is right. The market rallies, and you sell out at 4222
- 4222 – 4202 = 20. 20 points x £1 a point = a profit of £20
Example 2. Losing Bet
A losing spread bet trade
- The Gold price is quoted at $1,850 – $1,851
- You’re expecting prices to fall, so sell at $1,850, risking £1 a point
- However, the market rises, and you sell out at $1,855
- $1,850 – 1,855 = -50 x £1 a point = Loss of £50
What Is A Stake Size and Spread?
There are various terms which you will discover and will need to understand when it comes to spread betting, two of which include stake size and spread.
We’ve touched on these briefly above, but we’ll describe them in more detail here.
Stake Size
In spread betting, you specify a fixed bet size (or stake) that represents the amount you want to risk or gain for each point of market movement. This fixed bet size determines how much you will profit or lose for every point the market moves.
For example, setting your bet size to £10 means that for every point the market moves, you will profit (or lose) £10. So if the market moves 10 points higher, you will make £100, and if the market falls 5 points against you, you will lose £50.
We have created a spread betting calculator to help you determine your position sizes.
Spread
The spread is the difference between the bid (buy) and ask (sell) price of the asset you pay to open a bet. As there is no commission, this spread is what the broker will make when you place a trade.
For example, If you want to buy USD/JPY and see a buy price at 150.50 and a sell price at 150.48, the difference between the two prices is two pips. So, if you wanted to stake £10 per point on USD/JPY, it would cost you £20 to enter the bet.
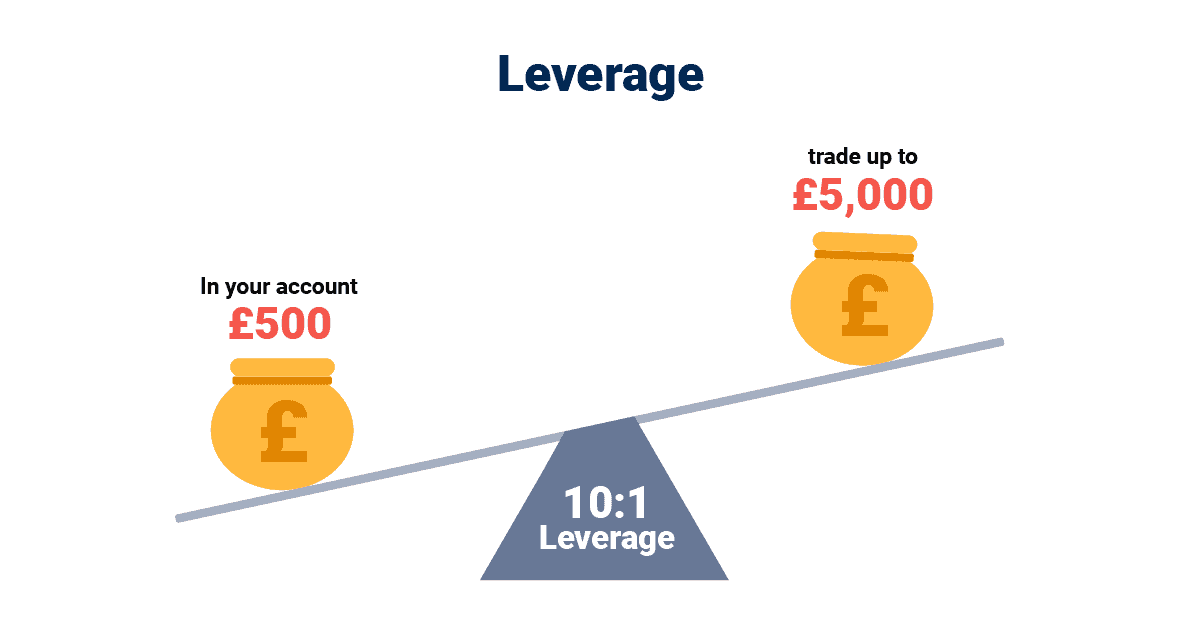
What Is Leverage?
Leverage in spread betting refers to the ability to control a larger position size in the market with a relatively smaller amount of capital. This means you can amplify both potential profits and losses, so it’s important to understand and use it responsibly.
The use of leverage is a fundamental aspect of spread betting and is expressed as a ratio, such as 1:10 or 1:100. If you’re a retail account holder – which most spread bettors are – you’ll be able to leverage up to 1:30.
With a leverage of 1:10, every £1 you place as your collateral (known as your margin) provides you with £10 worth of exposure to the market. Therefore, if the position size is worth £1,000 the broker will request a £100 margin from you.
How Long Is The Bet Duration?
Bet duration in spread betting refers to the timeframe for which a spread bet remains open and active.
Different durations are available, from daily to monthly spread bets. We advise you to keep in mind that costs can vary depending on the bet duration.
For example, the most common spread bet is called a Daily Funded Bet (DFB). This is a short term bet, and typically has the lowest spreads available, but will incur rollover fees if you keep the bet open overnight.
These overnight fees can be expensive. As an alternative, some brokers offer monthly spread bets with wider spreads but lower (or no) rollover fees. In our experience, this is a better choice if your prediction runs for a longer period.
How Does Going Short and Long Differ?
As a derivative, spread betting allows you to speculate on market movements without owning the underlying asset. You can go long (buy) at the market price if you anticipate the market rising, or go short (sell) if you expect declines.
This flexibility is particularly advantageous for short-term traders, enabling them to capitalise on daily market volatility by taking both long and short positions throughout the day. Additionally, you can choose to go long and short on different instruments at the same time – a strategy commonly known as hedging.
What Are The Margin Requirements?
Margin in spread betting refers to the minimum amount of money that you need to deposit to open and maintain a leveraged position.
It is a percentage of the total position size and serves as a security against potential losses which you might incur.
What Markets Can You Spread Bet?
Spread betting provides access to a diverse range of financial markets, allowing you to speculate on the price movements of various instruments including:
- Forex (Foreign Exchange): Major currency pairs such as EUR/USD, GBP/USD, and USD/JPY are popular choices for spread betting, but you will have a vast range of major, minor and exotic pairs to choose from.
- Stocks: Most spread betting providers offer you the ability to speculate on the price movements of individual stocks. This means you can trade major US companies and potentially smaller companies from other jurisdictions as well.
- Indices: You will also be able to bet on the performance of stock market indices, such as the FTSE 100, S&P 500, or DAX, along with other indices like the US Dollar index (DXY). This enables you to take a position on the overall performance of a market index.
- Commodities: Spread betting covers a range of commodities, including precious metals (gold, silver), energy commodities (oil, natural gas), and agricultural commodities (wheat, corn).
- Interest rates: Some spread betting brokers will also offer interest rates for you to trade, although these markets are generally less popular than forex and stocks.
What Market Can You NOT Spread Bet?
The FCA prohibits trading on some highly volatile markets. If you’re a retail account holder, you are not permitted to spread bet on cryptocurrencies.
For professional traders, crypto spread betting is permitted. However, if you qualify for this, you will waive all the protections offered by the FCA – such as negative balance protection. Of the broker’s we’ve tested, only Spreadex offers crypto markets to its professional spread bettors.
Who Are The Best Spread Brokers?
Pepperstone – Best Overall Spread Betting Broker
We like Pepperstone and rate it as the best spread betting platform in the UK based on our tests. The broker excelled, thanks to fast execution speeds, low spreads and a decent range of markets.
The broker offers 62 currency pairs, 1,000 stocks, 25 commodities, and 28 indices with low spreads from 0.7 pips on EURUSD.
Pepperstone supports several popular trading platforms, including MetaTrader 4, MetaTrader 5, cTrader and TradingView. If you are heavily invested in technical analysis, we recommend you try TradingView with Pepperstone.
Other brokers we recommend checking out include City Index, IG Group, FXCM, FxPro, OANDA, CMC Markets and Spreadex. All of these performed rather well in our testing.
Pepperstone ReviewVisit Pepperstone
75.3% of retail investor accounts lose money when trading spread bets and CFDs with this provider.
FAQ
Which Trading Platform Is Best For Beginners?
Of all the brokers we have reviewed, we think Pepperstone is the best performing broker overall, due to the low spreads, great range of markets and ease of use.
Does Anyone Really Make Money From Spread Betting In The UK?
Like any form of investing and trading, spread betting is risky. Some traders make money, while others don’t.
If you’re able to demonstrate consistent skill and discipline, then you will have a greater chance of making money when spread betting. As spread betting is tax exempt, you’ll also be able to keep more of any profits you do make.
What Is The Difference Between Spread Betting And CFD Trading?
Spread betting and Contracts for Difference (CFD) are both derivative products that allow you to speculate on financial instrument price movements without owning the underlying assets.
There are many similarities but also some key differences, namely that spread betting is only available for UK residents and any gains made are tax-free.
Is Spread Betting Risky?
Using any type of derivative involves some degree of risk. This is why we strongly recommend thorough research into the products, brokers and markets available.



Ask an Expert
How do I calculate my potential profit or loss in spread betting?
You multiply your stake size by how far the price moves in your favor or against you to calculate profit or loss.