In the UK, spread betting is regulated by the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA), which I consider to be one of the most respected financial regulators globally. In this article, I share how financial spread betting is regulated in the UK and what the FCA does to protect your funds while keeping brokers accountable.
What Are The FCA Spread Betting Regulations?
Set up as part of the Financial Services and Markets Act 2000, the FCA has established comprehensive regulations for spread betting firms operating within the jurisdictions of the UK. These regulations cover various aspects of the broker, from financial requirements to advertising standards.
All brokers in the UK must be regulated by the FCA if they wish to provide financial services to UK traders. Let’s look at some of the key areas the FCA addresses.
1. Financial Requirements
One aspect of FCA regulation that I find particularly important is the financial requirements imposed on spread betting providers, ensuring the stability of the companies you bet with.
The FCA ensures all firms maintain adequate capital reserves. This is essentially a safety net to ensure the broker can meet its financial obligations, even in turbulent market conditions.
Additionally, an FCA-authorised firm is required to provide regular financial reports to the FCA. In my opinion, this ongoing oversight helps to catch potential issues before they become major problems.
Another interesting aspect of the financial requirements is the stress testing that firms must undergo. I think this is a smart move by the FCA, as it ensures that spread betting companies can withstand various market scenarios without putting your funds at risk.
Our list of the best UK forex trading platforms only lists FCA regulated brokers due to the trust and features the regulator offers UK residences.
2. Providing Advice
The FCA takes providing financial advice very seriously and strictly regulates this service to prevent market abuse. The broker and the person providing the advice must be authorised in order to provide legal financial advice.
Typically, the person will have gained certification to provide financial advice to retail customers, which can take months to complete. This certification prevents misleading or biased information from influencing our trading decisions, so not every firm can legally tell you what trades to make or how to manage your portfolio.
In fact, these types of advisory services are offered to premium members or specialist advisory brokers instead of the execution-only brokers you’d typically use for spread betting, like Pepperstone.
To give you an idea of what this looks like in practice, here’s a comparison of permitted vs. prohibited advisory practices:
| Permitted | Prohibited |
|---|---|
| Providing factual market information | Recommending specific trades without proper authorisation |
| Explaining how different financial instruments work | Guaranteeing profits or downplaying risks |
| Offering general trading education | Providing personalised investment advice without proper qualifications |
3. Equal Playfield
The FCA mandates fair treatment of all clients, regardless of their account size or trading experience, which I think is crucial for maintaining trust in the spread betting industry.
Investment firms are required to have transparent pricing and execution policies so you can have a clear understanding of how your trades are priced and executed.
When you review a broker like SpreadEx, you’ll notice they have a “Best Execution Policy”. This policy details how they ensure you will always get the best possible price at the time of execution, even if it’s better than the price you requested. If you end up with a better price requested, this is called positive slippage.
4. Advertising Content
The FCA has some of the strictest standards in the financial industry and is crucial for protecting traders, especially if you’re new to spread betting.
When it comes to brokers advertising their financial promotions, the FCA requires all advertising to be clear, fair, and not misleading. Doing this helps to prevent unrealistic expectations and ensures that you accurately understand what we’re getting into.
One important introduction that FCA has mandated is the use of prominent risk warnings, highlighting the level of risk with spread betting and how many spread bettors lose money.
A knock-on effect of these advertising standards made promotional offers like bonuses harder to offer in the UK, as these offers were notorious for having high requirements to withdraw your funds. I think the FCA’s approach helps to prevent traders from being lured in by flashy promotions without fully understanding the risks involved.
5. Leverage Limits
The FCA has acknowledged the potential risks of leverage with retail traders in spread betting and has taken steps to protect retail traders from overleveraging.
The FCA has introduced restrictions on leverage for retail traders, which can protect you from taking on too much leverage that can wipe out your account in seconds if you are unprepared.
These leverage limits differ for each asset class, reflecting the volatility and risks associated with the financial instrument.
Here’s a table showing the maximum leverage ratios for different asset classes:
| Asset Class | Maximum Leverage for Retail Clients |
|---|---|
| Major Forex Pairs | 30:1 |
| Minor Forex Pairs | 20:1 |
| Gold | 20:1 |
| Major Indices | 20:1 |
| Commodities (excluding gold) | 10:1 |
| Individual Equities | 5:1 |
6. Client Suitability
The FCA requires spread betting firms to assess each client’s knowledge and experience before allowing them to trade. This suitability test typically involves an appropriateness test for complex financial instruments like spread bets and ensuring the client can afford to lose money.
These questions are embedded with every broker’s account opening process, which is why they ask for your financial/employment details and a questionnaire on your trading knowledge.

7. Complaint System
To improve transparency and fairness, the FCA requires firms to have clear and effective internal complaint-handling procedures. I think this is crucial for resolving issues quickly and fairly.
If a complaint can’t be resolved internally, you can escalate it to the Financial Ombudsman Service. This system can be an invaluable resource for impartial dispute resolution when you are getting nowhere with your broker complaint.
Another interesting point is that firms are required to report complaints to the FCA regularly, which helps the regulator identify any systemic issues in the industry.
Here’s a typical complaint resolution timeline based on the FCA’s expectations:
- Initial complaint to firm (0-3 days)
- The firm acknowledges complaint (within 5 business days)
- The firm investigates and responds (within 8 weeks)
- If unresolved, the complaint is referred to the Financial Ombudsman (within 6 months of the firm’s final response)
- The ombudsman investigates and makes a decision (typically within 90 days)
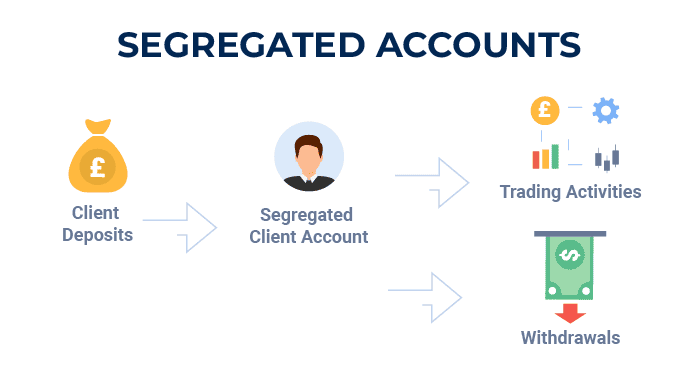
8. Segregated Accounts
Spread betting firms must hold client funds separately from company funds, protecting your money in case the firm encounters financial difficulties.
In my opinion, the FCA’s requirement for segregated accounts is one of the most important protections for all spread betting companies.
Regular audits are conducted to ensure the broker remains compliant with these rules, helping maintain the integrity of the segregated account system.
To illustrate how segregated accounts work, here’s a simplified diagram:
Recent FCA Regulatory Changes
The FCA has made several new rules that have generally been positive for retail traders in protecting high-risk derivatives like spread betting and Contracts for Difference (CFDs).
One of the most impactful changes has been implementing stricter leverage limits, reducing the maximum leverage from 500:1 to 30:1 for retail traders on foreign exchange markets. While this might seem restrictive initially, I think it helps protect you from excessive risk and overleveraging your positions that may cause you to lose money faster.
A change that impacts how brokers advertise was also introduced. Now, brokers must show standardised risk warnings to show the risk associated with spread betting while also showing the profit/loss ratios on client accounts. Additionally, brokers are not allowed to offer new deposit bonuses in the UK as an incentive to sign up with them, which was common practice a few years ago.
Finally, brokers are required to offer negative balance protection, which ensures you cannot lose more than the total funds in your trading account and prevents you from owing the broker money.
Here’s a comparison of key regulations before and after recent changes:
| Aspect | Before | After |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum Leverage | Up to 500:1 | 30:1 for major forex pairs, lower for other assets |
| Risk Warnings | Less prominent | It must be clearly visible and include specific risk percentages |
| Bonus Offers | Common practice | Heavily restricted or prohibited |
| Negative Balance Protection | Not mandatory | Required for all retail clients |
You can keep up to date on the FCA’s updates on the official website: fca.org.uk
How To Choose A UK Spread Betting Platform
As someone who’s tried various spread betting platforms over the years, I’ve developed a few key criteria for choosing the right one. Here’s what I look for:
- FCA regulation and authorisation: Every UK broker is regulated by the FCA if they offer spread betting, but you should always double-check.
- Competitive spreads and fees: I compare the costs across different spread betting platforms, as these can significantly impact profitability over time.
- Available markets: I like platforms that offer a wide range of markets to trade, allowing you to trade various financial markets with one account.
- Choice of trading platforms: I make sure the broker offers a solid choice of trading platforms, such as MetaTrader 4 and TradingView.
- Customer support: In my experience, responsive and knowledgeable customer support can be invaluable, especially during critical trading moments, so ensure they have a responsive live chat.
- Educational resources: I appreciate platforms that offer comprehensive educational materials for new traders or daily market update webinars to keep you in the loop on market news.
If you’d like a starting point on some of the best spread betting platforms that meet these requirements, check out some of my top picks below.
| Platform | My Score | Min. Deposit | Min. Trade Size | Trading Platforms | Demo Account |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pepperstone | 98/100 | £0 | £0.50 per point | MT4, MT5, cTrader, TradingView | Yes |
| Spreadex | 96/100 | £0 | £1.00 per point | Spreadex Trading Platform, TradingView | Yes |
| OANDA | 91/100 | £0 | £0.01 per point | OANDA Trade, MT4, TradingView | Yes |
| IG | 86/100 | £250 | 0.50 per point | IG Trading Platform, MT4, ProReal Time | Yes |
What Tax Applied For Spread Betting?
The most attractive feature of spread betting is its tax treatment in the UK. Spread betting is considered a “gambling product” in the eyes of UK tax law, so it is exempt from capital gains tax. This exemption means you do not pay tax on your profits, which can boost your overall profits compared to traditional investing methods like trading CFDs.
Although a “gambling product” for tax purposes, the Gambling Commission in England do not regulate the product. Instead, it is considered a financial activity that falls under the FCA’s oversight.
In addition to capital gains tax, spread betting is also exempt from stamp duty as it does not involve purchasing an asset, further lowering its trading costs.
However, I think it’s important to note that this tax-free status may change if spread betting becomes your primary source of income. In such cases, HMRC might view your activities as a business, which could have different tax implications.
It’s also crucial to remember that tax laws can change, and individual circumstances may vary. I always recommend consulting with a tax professional for personalised advice.
To illustrate the potential tax differences, here’s a simplified comparison of tax implications for spread betting vs traditional investing:
| Aspect | Spread Betting | Traditional Investing |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Gains Tax | Exempt | Applicable on profits |
| Stamp Duty | Not applicable | 0.5% on UK share purchases |
| Income Tax | Not applicable unless deemed a business or sole income | Applicable to dividends above the allowance |
If you’re new to trading, then we recommend selecting one of our shortlisted beginner spread betting brokers in the UK.



Ask an Expert
Do professional spread bettors have different regulations?
Yes, professionals might not have the same protections as retail traders, like lower leverage caps.
Are there regulations for spread betting on cryptocurrencies?
Yes, even crypto spread betting can be regulated, but it depends on the broker and where they’re based.