Spread betting works by tracking the price or value of an underlying asset, so that you can speculate on the price movements of the asset without owning the asset itself. If your bet correctly predicts the price movement of the chosen financial (or sports) market, then profits can be achieved from the difference between the price you opened and closed your bet.
To open a spread bet, you must pay a spread, which is the difference between the broker’s sell and buy prices. If you think the markets will rise, you will buy, and if you think they will fall, you will sell the markets.
1. Going Long or Short
Spread betting allows you to profit in bullish (rising) and bearish (falling) markets, making it a valuable tool for day trade. The broker allows you to go long if you think the spread betting market will rise or short if you think it will fall.
2. Leverage and Margin
Leverage allows spread bettors to control larger bet sizes with small funds so you can increase your profits (and losses) with smaller market movements. The leverage makes day trading accessible, especially for those with small-spread betting accounts, allowing you to leverage up to 30 times your capital per bet. With this in mind, leverage is a high risk as it can magnify your wins and losses with small market movements.
Margin is what the spread betting broker requires from you as collateral to open a spread bet through leverage. The required amount of margin differs for each asset and is the minimum amount you must have in your account before opening a bet.
3. The Spread
The spread is the difference between the buy and sell price and is charged by the broker to cover its services to you. For example, the spread on EURUSD can be seen as 1.0750/1.0749, showing a one-pip difference, which is the spread. If your bet size is £10 per pip, entering this EURUSD bet would cost you £10.
4. Bet Sizes
Bet sizes (stakes) are the amount you want to risk per point. The price moves in your favour and can range from 1p to £1,000 per point of bet sizes. For every point the market moves, you will make (or lose) the stake, i.e.) if the bet size is £1 and the market moved 10 points, you make £10.
5. Bet Duration
There are two types of spread bet durations:
The first is a daily funded bet (DFB) with no expiration period, but you are charged rollover fees (based on the interest of the leverage borrowed). DFBs are ideal for intraday trading and short-term trading ideas because the spreads are tight, and you can save money by closing the bet before midnight.
The second is the futures bet, which expires every quarter; these have high spreads to execute but have lower overnight fees, making them ideal if you have a longer-term trade idea.
Spread Betting Beginners Guide
There are many ways to learn how to spread bet, and choosing the best may seem like a task. Below, I’ve cultivated a simple guide for beginners to get started with spread betting:
Step 1: Open a demo account
As a beginner, starting with a spread betting demo account from one of the top FCA-regulated brokers like Pepperstone would be best. You can use this account to learn how to execute bets and analyse the markets without making a deposit or risking your capital.
Step 2: Learn about technical analysis
You should find spread betting courses discussing how to use technical analysis to find market opportunities. Technical analysis is a popular method as it can help identify trades in lower timeframes like the 5-minute or 15-minute timeframes, both providing excellent opportunities for day trading.
Learning about fundamental analysis can be vital if you want to understand why the markets are moving and how they can impact the price during the day. However, it is unnecessary if you are spread betting on a small timeframe.
Step 3: Learn about risk management
Risk management is the art of protecting your capital, and you should know the basics before you decide to risk your hard-earned money. You’ll find that it’s relatively simple, and you can set up orders like stop losses and take profits to manage your risk automatically.
Step 4: Develop a trading strategy
Once you have learned how to use technical analysis and risk management, you should combine them to create your trading strategy. The trading strategy is your path to building consistent profits by following the rules you’ve applied within the strategy, which should generate the results.
Step 5: Put in the practice
It goes without saying, but if you want to profit from spread betting, you have to put in the hours to get the experience of the markets. You should practise your trading strategies and risk management on a demo account to improve your skills and recognise opportunities faster.
When finding trading ideas becomes routine, and you don’t have to double-check your strategy to ensure it’s a valid signal to bet, you’ll be ready to bet on live markets.
Step 6: Go live and start small
When you have developed a consistently profitable trading strategy and experience on the demo account, you should be comfortable to risk your capital. This is where other psychological factors come into play, such as fear of losing money or chasing losses.
So, I recommend you start small with your bet sizes and work your way up as your confidence grows. At the end of the day, you are earning (and losing) pips, so focus on this instead of how much you are winning in capital.
For a more extensive guide, you should check out my spread betting guide to learn more about how to take advantage of it.
Spread Betting How To Video Guide
What Is Spread Betting?
Spread betting is a form of derivative trading where you can speculate on the future price movements of different financial instruments. Rather than buying or selling the underlying asset, you are betting on which way markets move, making a profit if your predictions are correct.
For example, if you believe an asset’s price will increase, you may bet a stake of £10 per point of movement. If your prediction is correct, meaning the asset’s market price increases, your profit will equate to your £10 stake x the number of points the market moves. If your guess is wrong, you will lose your stake x the number of points the market moves.
- Bullish: You buy (go long) the asset if you are betting the market price will increase in value.
- Bearish: You sell (go short) the asset if you are betting the market price will decrease in value.

How To Place A Spread Bet
To place a spread bet is straightforward, but you must have a registered spread betting account and a trading platform first.
Step 1: Choose A Market
Pick an ideal market you want to spread bet on, and there is a range of markets to choose from, with spread betting companies offering forex, commodities, shares, and indices. Personally, I like betting on forex pairs like EUR/USD and GBP/JPY as they provide plenty of opportunities to spread bet during the day.
Step 2: Decide To Buy Or Sell The Market
Once you find a market to bet on, you should perform your analysis to find a new trading idea. You can perform technical analysis using indicators and chart patterns to find a new opportunity or fundamental analysis to find which markets are bullish or bearish. Depending on your analysis, you will choose to buy or sell the market.
Step 3: Choose Your Bet Size And Execute
After finding your trading idea, you will open a deal ticket and enter your bet size (stake) into the deal ticket. This is the amount you wish to win (or lose) every point the market moves. Once you’ve set up the deal ticket, click ‘place trade’ to execute the order, and the broker place the bet for you.
Step 4: Monitor And Close Your Bet
While the bet is open, you can monitor its movements and judge when you want to close it for profit or loss. You can automate this by setting up a stop loss, automatically closing the position if the market moves against you, limiting your losses.
What Are The Benefits Of Spread Betting?
There are many benefits to using spread betting to speculate on the markets. Its main advantages of spread betting are that it is tax-free, can be used on a wide range of markets, and has low trading fees compared with alternative choices like CFD trading.
Tax Fee
Spread betting is considered a gambling product by the HMRC, making the winnings (profits) generated by spread betting exempt from capital gains tax, saving you up to 20% on tax. It is also a derivative (don’t own the underlying asset), meaning you will not pay the stamp duty tax either, saving you a further 0.5% tax on purchases.
No Commissions
Another advantage of financial spread betting is that you do not pay commissions on your bets. Instead, you only pay a spread to execute your orders, keeping your costs simple with the best spread betting brokers offering spreads from 0.5 pips on EURUSD.
Pros and Cons of Spread Betting
| Pros | Cons |
| Tax-Free profits | Leverage can lead to large losses |
| Leveraged trading | Can’t declare tax losses |
| Access a wide range of markers | Not for long-term investors |
| No commission | No dividends with shares |
| Profit from rising and falling markets | Overtrading |
| Not limited to contract sizes in lots | Risk of account closeout |
| Bet in GBP, no currency conversation fees |
What Are The Risks Of Spread Betting?
With all investing methods, spread betting risks are similar: you can lose money should the market move against you. As spread betting uses leverage, it can amplify your losses from the smallest market price movement.
For example, if you had a leverage of 1:10 and controlled a £1,000 position with just £100, a 10% decrease of £1,000 would wipe out your margin. So, you have to have solid risk management in place to protect your losses while spread betting and using leverage.
How To Managing Risk in Spread Betting?
Spread betting providers will offer different risk management tools that will help you capture gains and minimise losses. This matters because financial markets experience high levels of volatility, meaning there are risks to consider, such as gapping and slippage.
Gapping is where the price jumps from one price to another without passing through the price level in between. Slippage is when there is a price change between when you place your order and when it is executed.
Order types are one such tool to utilise to protect yourself against volatility and gapping. Examples of such order types include stop-loss orders and guaranteed stop-loss orders.
1. Standard Stop-Loss Orders
Stop loss orders allow you to set a predetermined price where your order is automatically closed if that price is met. A stop-loss aids in minimising losses but doesn’t guarantee your order will be closed at your predetermined price, which can occur due to gapping or slippage.
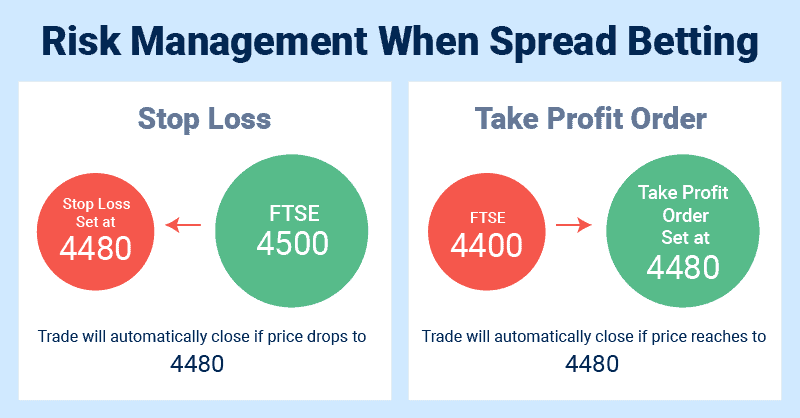
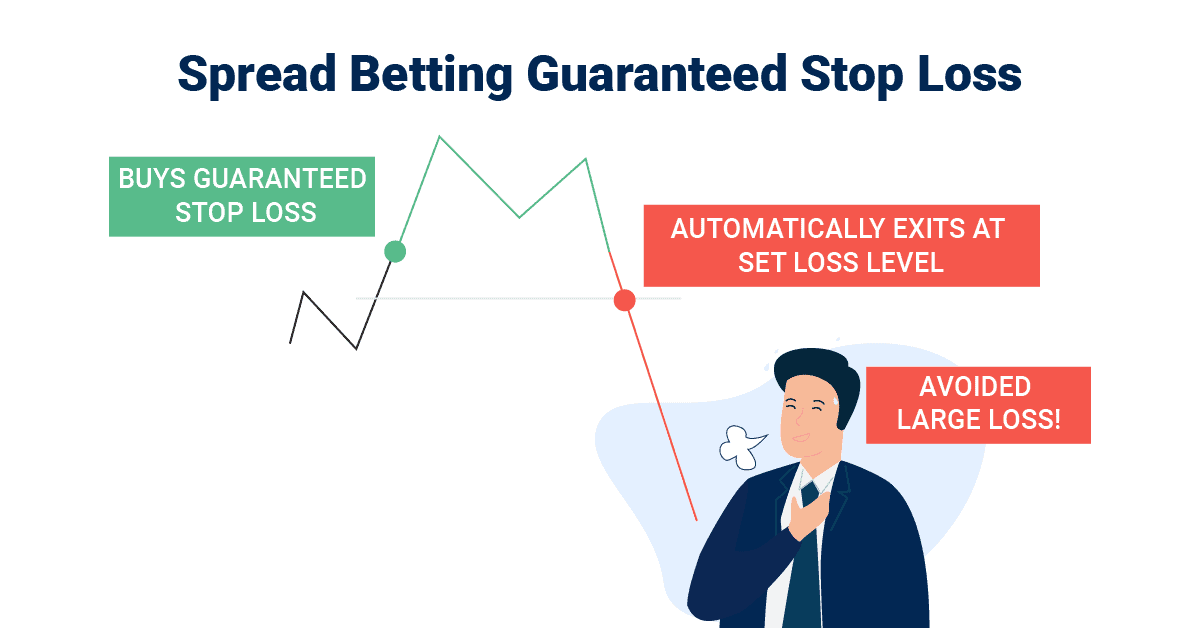
2. Guaranteed Stop-Loss Orders
Guaranteed stop loss orders are the same as normal stop losses, except the broker guarantees your order will be closed at your predetermined price, regardless of volatility or gapping.
Spread Betting Example: Buying FTSE 100
Let’s take a look at buying the FTSE 100 as a spread betting example:
FTSE 100 price is 7440, and you believe the price will rise based on your technical analysis. To enter the bet, you place a buy bet of FTSE 100 at 7740 and stake of £5 per point. This means for every point the price rises above 7000, you will make £5 per point, while for every point below 7000, you will lose £5 per point. You set your take profit at 20 points (7460) and stop loss for 7430, giving you a risk of 10 points vs 20 points profit.
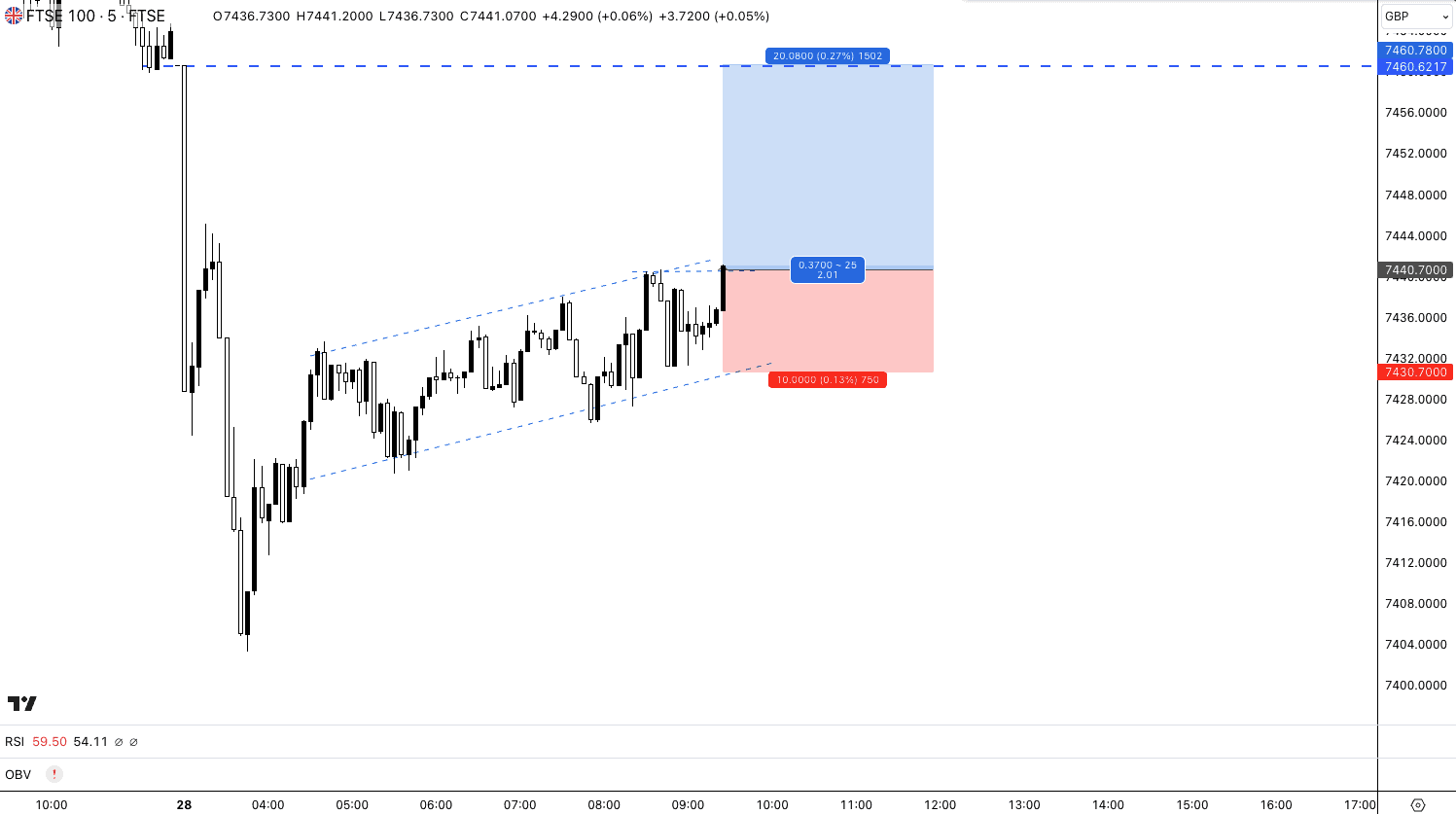
The price of the FTSE increased as per your prediction, rising to 7460 (or 20 points increase), and your take profit order was executed, closing the bet. Your profit is your stake size x the number of points increased (£5 x 20 points), making you a £100 profit.
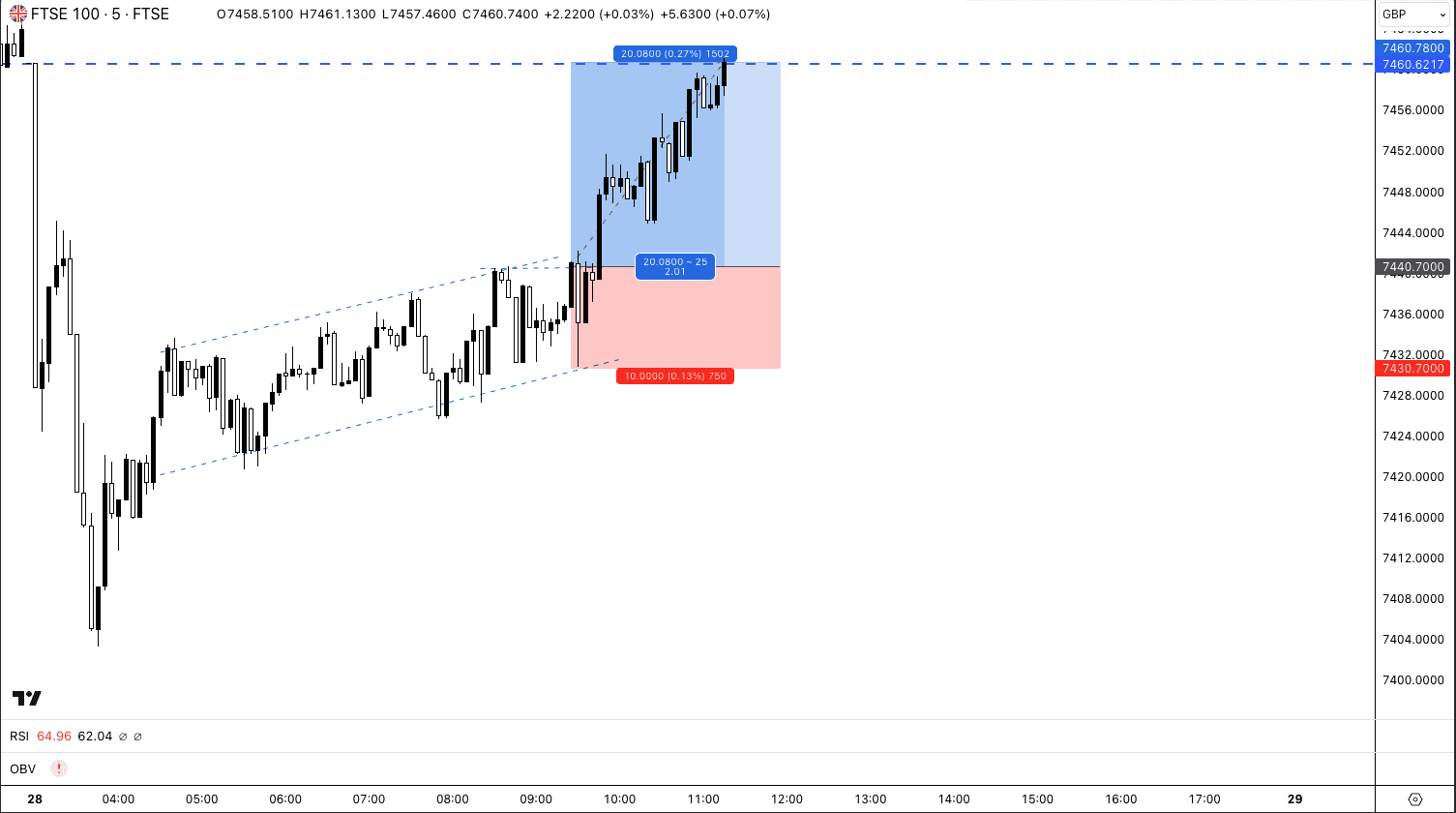
If the FTSE 100 price fell to 7430, you would have lost your stake size x the amount of points decreased (£5 x 10 points), causing a £50 loss.
Spread Betting Example: Selling Gold
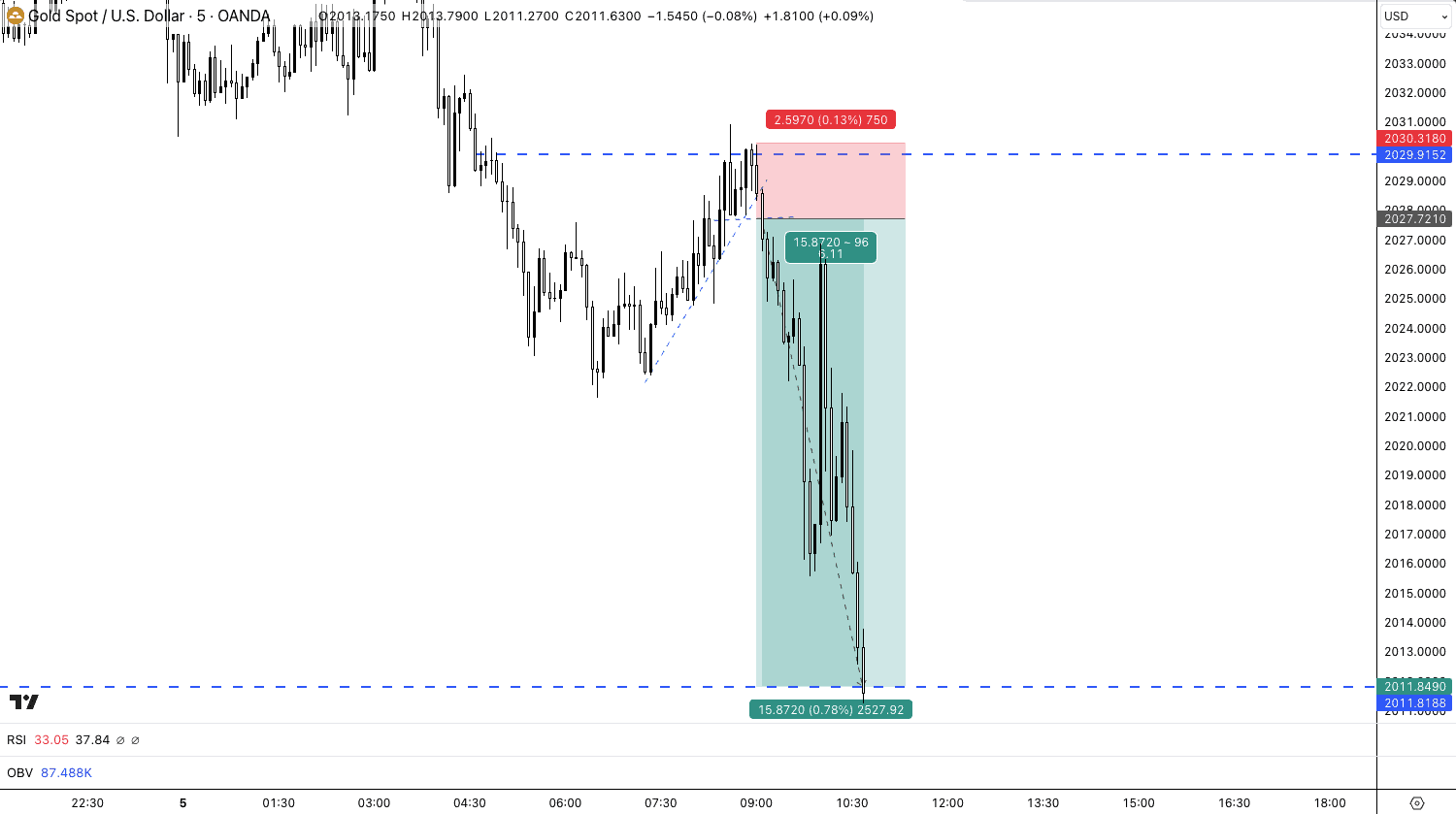
In spread betting, you can profit when markets fall in value, so I’ll go over how you can profit when the price of gold falls by placing a sell spread bet.
The price of gold is trading at $2027, and you believe that the price will fall because of your fundamental and technical analysis. To enter the bet, you place a sell bet of gold at $2027 and stake £1 per point. One point of gold equates to a $1 move in price, so for every $1 below $2027, you will make £1 profit, and for every $1 above, you’ll lose £1.
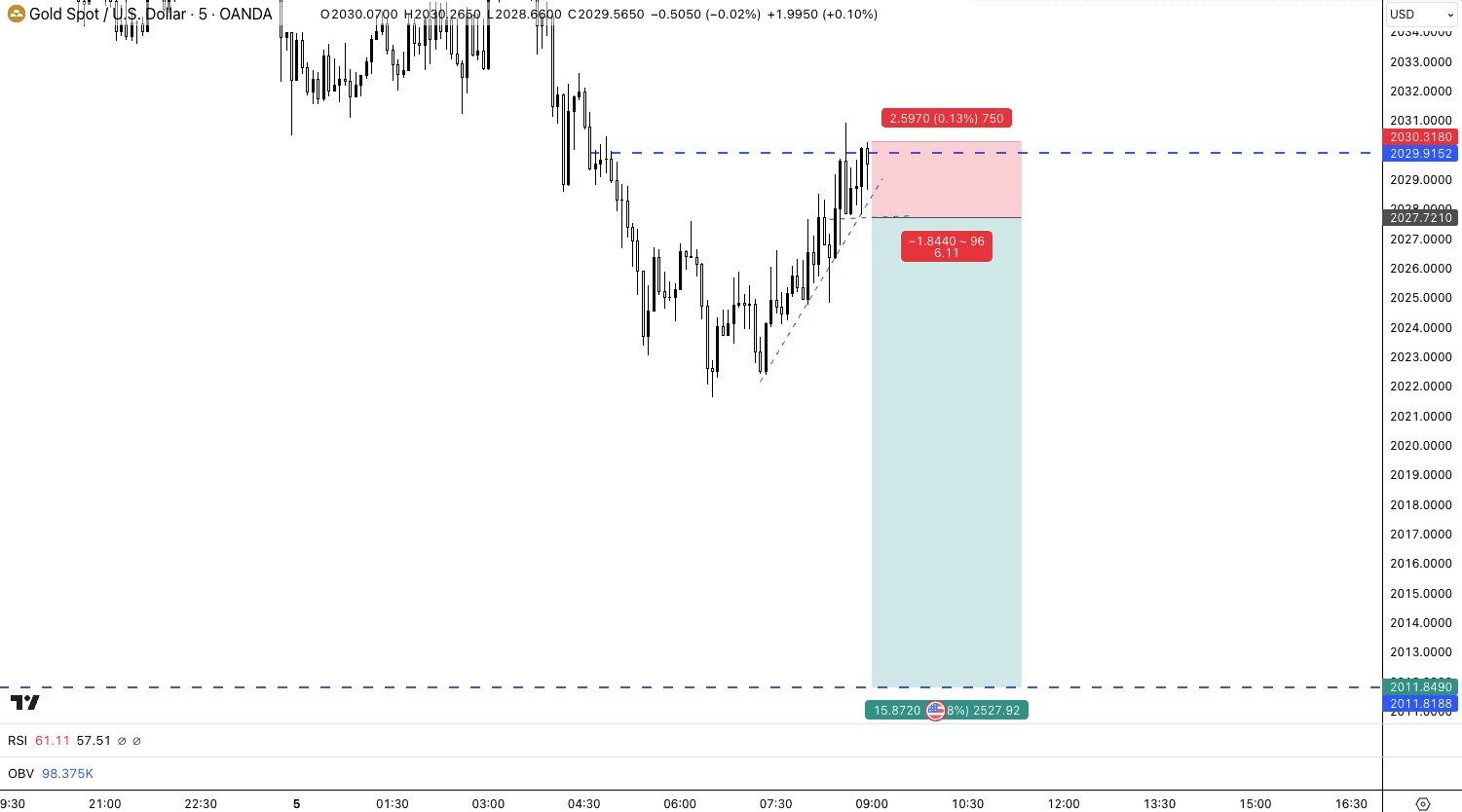
The price of gold fell to $2012 in an hour, netting a $15 price fall (15 points), meaning you made £15 profit (£1 per point x 15 points). Should the price increase instead to $2030, you would have lost £3 (£1 per point staked x 3 points increased).
FAQs
What Are The Origins Of Spread Betting?
Spread betting was brought to traders in the UK by IG Group in the 1970s by Stuart Wheeler (the founder of IG Group), who was an investment banker. It was used so individuals could speculate on the price of gold without owning or receiving the physical commodity. Nowadays, spread betting has expanded to every financial instrument, from stocks, commodities, indices, and currency markets.
Is Share Trading Better Than Spread Betting?
This depends on personal preference; share trading offers this if you want to receive the perks of being a shareholder (like voting rights and dividends). Additionally, you can net off your share trading losses against your taxes, therefore reducing your overall tax liability.
However, spread betting shares have lower trading fees – you do not have to pay commissions, stamp duty or capital gains tax. You can also bet on any market using GBP to access US and EU shares with the benefits of UK taxes and no currency conversion fees.
Finally, spread betting has leverage, meaning you can easily bet on shares and profit from smaller market movements by using less capital than with share trading.
How Do Spread Betting Companies Make Money?
Spread betting companies make money through the spread. The spread has a small markup, meaning the difference between the broker’s sell and buy price is widened by a small amount, and this difference is the broker fee for their service.



Ask an Expert
Is spread betting riskier than regular trading?
It can be riskier due to leverage, but with proper risk management, you can control that risk.